

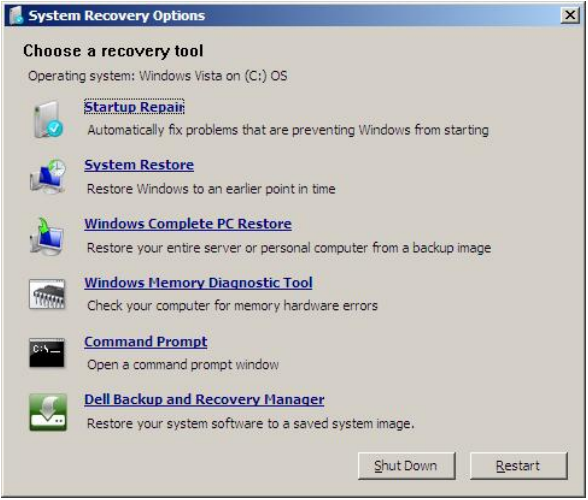
To do this you click on Settings > Update & Security > Recovery (left pane) > Get Started. This will remove apps and settings, but keep your personal files if you wish. Then press apply.Īlternatively, you can reset your system or reinstall Windows. This will determine how much of your hard drive to use in restoring. Enable the turn on the system protection’ button and move the Max Usage slider to around 5-10%. Type in System Restore in the search bar and click create a restore point.’ Then in the system properties pop up click on the System Restore button. To do this click on the Start/Windows button in the bottom left of the screen.
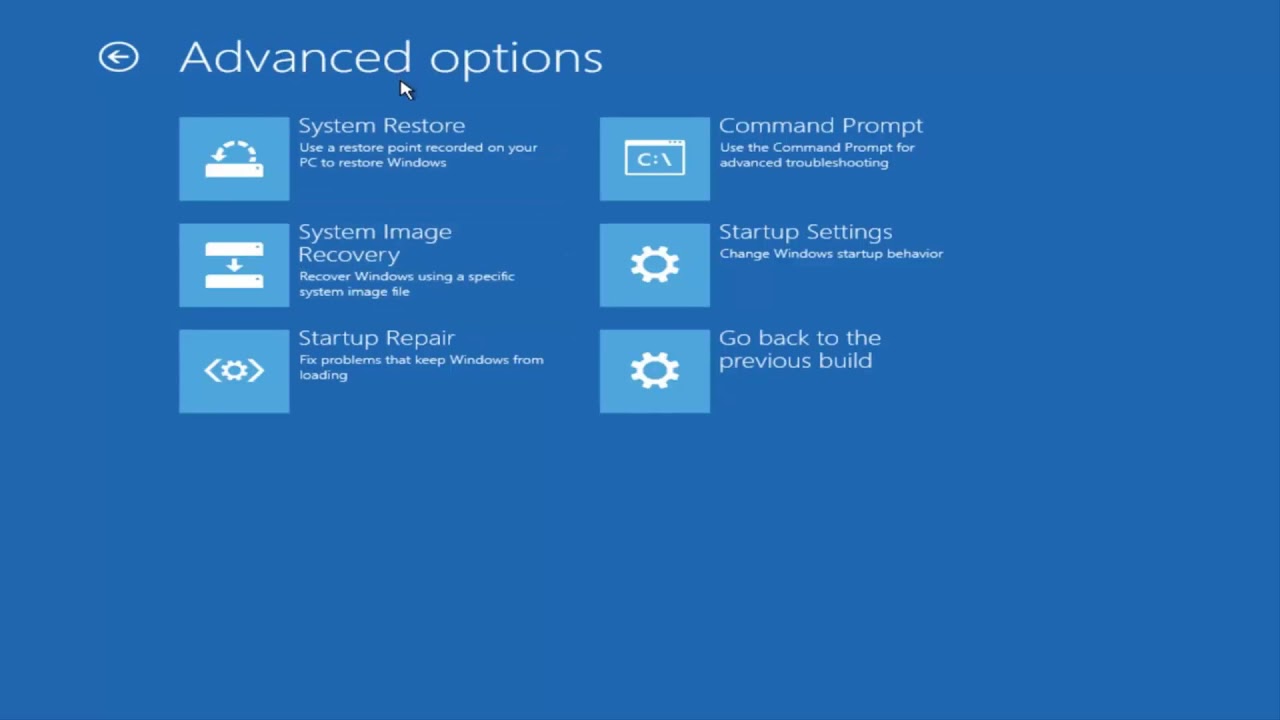
If all the steps above haven’t helped running the system restore tool will restore your operating system files to a previous state, a time where the files were not corrupt. If a change has been made, restart your computer and run the System File Checker command and hopefully it should now replace any corrupt files.
A message will then appear outlining if a change has been made. The progress bar initially may be slow, but do not cancel the command. Then click Command Prompt (Admin).’Īgain, this will take 5-10 minutes. To do this, right-click on the Windows/Start button in the bottom left corner of your screen. To start the process, you will need to be in the Administrator Command Prompt window. But how do I run the System File Checker!? So if they can’t be fixed by the File Checker it is likely that the DISM can fix the underlying system, allowing the checker to then run correctly. However, problems associated with the System File Checker are also associated with DISM. The DISM option is second as these problems are less common. If that doesn’t work the second option should always be the DISM command. However, if it does not fix the problem it will then eliminate the possibility of your system files being corrupted and will allow you to use other methods. Use the System File Checker command first as it will solve the most common problems.
#Windows system recovery windows 10 cmd how to
To see how to fix this issue, either watch the video or read the instructions below: What option should I use first?
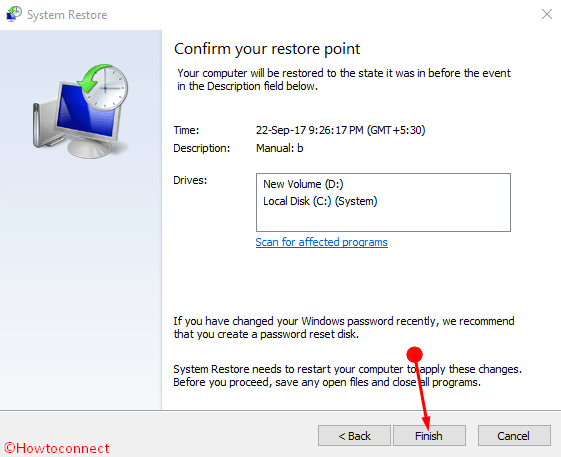
DISM stands for Deployment Image and Servicing management. If, however, the System File Checker fails to replace your file there is a second option. Windows will then go on to replace any files that have been modified or corrupted with the correct and original version of this file. This checker scans your system files, alerting you where there is corruption or any other changes. Windows, aware of this problem, have built a System File Checker in their latest update of Windows 10. I hope this article helped you! Please share it with your friends also.Ever been power typing on your keyboard with 100 tabs up on google, trying to get a really important piece of work finished and this horrific blue screen pops up? The immediate reaction for many is ‘why on earth did I not save that file’ or ‘please please please can this not be due to a corrupt file.’ If it is the latter, we know how you feel and are here to tell you how to fix it. However, you can’t roll back your Windows to the previous working state if you delete the restore points. You need to type in ‘Y’ and hit the Enter button on the confirmation prompt.Ĭreating and deleting system restore points is pretty straightforward. Also, note down the shadow copy ID of the restore point you want to delete.Ĥ. You need to look at the creation date and time. The above command will list all system restore points. On the command prompt, enter the command shared below:ģ. Right-click on the CMD and select Run as administrator.Ģ. First of all, open Windows search and type in CMD. If you want to delete a specific system restore point, you need to use the Command Prompt. Delete Specific System Restore Point via CMD Important: You need to implement the same steps for every drive to enable System Protection. You need to click on the Delete button to delete all the restore points. Next, select the drive and click on the Configure button.ħ. On the System Properties page, click on the System Protection tab.Ħ. On the About settings page, click on the System Protection option.ĥ. On the left pane, click on the About section.Ĥ.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
